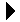There are many examples of problems that require the use of a map for storing and accessing data. That is, we need to associate a unique key with a data value in which the elements are accessed by key. Suppose you need to write a program that keeps track of the phone numbers in your mobile phone's contact list in which you lookup a number by name. You can use a map to store the entries where the names are keys and the phone numbers are values. A more classic example is the translation of state abbreviations in mailing addresses to their full name. Here, the abbreviations are the keys and the corresponding full names are the values. Consider the example map in Figure 2.8.1 of a small subset of state abbreviations.
Figure 2.8.1: An example map of state abbreviations.
Creating a Map
To create the map in the figure above, we start with an empty map
and then add each of the key/value pairs for the state abbreviations to the full name mappings. To add an element, you use the add method and provide both the key and the value
states.add("VA", "Virginia")
The order in which the key/value pairs are added does not matter since the elements are not stored in any particular order. We can add the four the additional mappings in any order
states.add("TX", "Texas")
states.add("NH", "New Hampshire")
states.add("FL", "Florida")
states.add("OK", "Oklahoma")
While the order in which the entries are made does not matter, it is important to note that the keys must be unique to the map. If you specify a duplicate key, the original value of that key is overwritten with the new value.
As with any container in Python, the len function can be used to determine the key/value pairs contained in the map.
print("The map contains", len(states), "entries.")
Modifying a Map
Suppose we associate the wrong state with an abbreviation when we enter it initially. Consider the statement
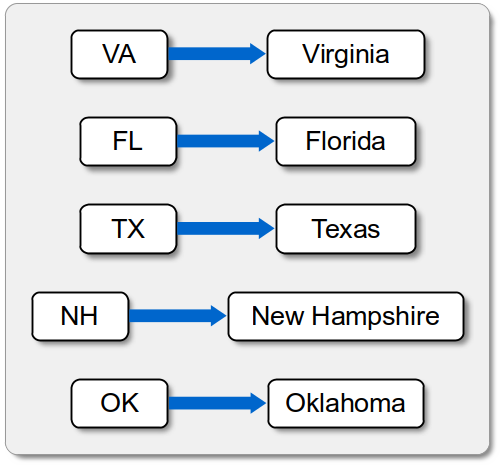
states.add("MS", "Massachusetts")
which results in a modified map with the new entry as shown in Figure 2.8.2 (a)
Figure 2.8.2: Modifications to the map: (1) the result of adding a new map entry and (2) the result after modifying the value of a key.
We can change the value associated with a given key by calling the add method with the existing key and a new value
states.add("MS", "Mississippi")
The original value associated with the key is removed and the same key now maps to a new value (see Figure 2.8.2 (b)). The key part of a key/value pair can not be modified. If you need to change a key, the element has to be removed and a new key/value pair added with the correct key.
Accessing Map Values
The valueOf method is used to return the value associated with a key. The statement
print("The state with abbreviation TX is", states.valueOf("TX"))
prints Texas for the state. Note that the map is not a sequence-type container like a Python list or the Polygon ADT, you cannot access the items by index or position. A value an only be accessed using its associated key.
The key supplied to the subscript operator must be a valid key in the map or an exception is raised. To determine whether a key is in the map, you would use the in (or not in) operator:
if "VA" in states :
print("The state with abbreviation VA is", states.valueOf("VA"]))
else :
print("VA is not a valid state abbreviation.")
For a more complete example, consider the code segment below which repeatedly prompts the user for a state abbreviation and displays the corresponding state or an error message:
abbreviation = input("Enter a state abbreviation:")
while abbreviation != "" :
code = abbreviation.upper()
if code in states :
print("The state with abbreviation", abbreviation, "is", states.valueOf(code))
else :
print(code, "is not a valid state abbreviation.")
abbreviation = input("Enter a state abbreviation:")
Removing Items
To remove an element from the map, call the remove method with the key as the argument:
This removes the entire element, both the key and its associated value (see Figure 2.8.3) If the key is not in the map, the remove method raises an exception. To prevent the exception from being raised, you can test for the key in the map:
if "Va" in states :
states.remove("Va")
Note that the if strings are used for the keys as in this example, the keys are case sensitive. Thus, in the previous example, the entry for Virgina would not be removed since its key is "VA" and not the incorrect one provided "Va".
Figure 2.8.3: Result of removing a map entry.
Clearing a Map
The Map ADT also provides a method to empty or clear a map. When the clear method is called
the entire contents of the map are removed, all key/value pairs.
Traversing a Map
If the iterator special method is implemented, you can iterate over the individual keys in a map using a for loop:
print("State Abbreviations")
for abbv in states :
print(abbv, states.getValue(abbv))
The result of this code fragment for our sample map from Figure 2.8.3 is shown below:
State Abbreviations
VA Virginia
MS Mississippi
NH New Hampshire
TX Texas
FL Florida