We indicated earlier that many different data structures can be used to implement a map. Since we are trying to replicate the functionality of the dictionary provided by Python, we don't want to use that structure. That leaves the use of a Python list.
To implement the Map ADT we must be able to store both a key component and the corresponding value component for each entry in the map. We can not simply add the component pairs to the list without some means of maintaining their association or mapping. There are two classic approaches for implementing a map when using an ordered sequence structure like the Python list.
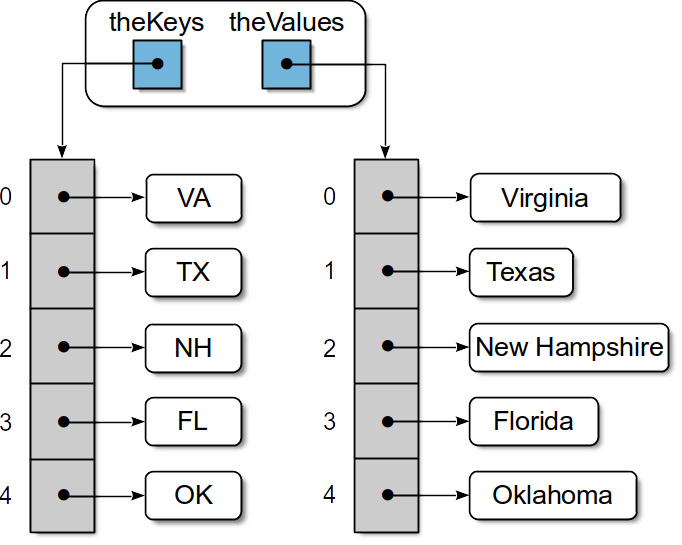
One approach is to use two lists, one for the keys and one for the corresponding values. Accessing and manipulating the components is very similar to that used with the Bag ADT. The difference, however, is that the association between the component pairs must always be maintained. To accomplish this, each key/value must be stored in corresponding elements of the two lists as illustrated in Figure 2.8.1.
Figure 2.8.1: Organizing the physical data of a map using parallel lists.
The constructor creates the two lists used to store the corresponding key and value components.
class Map :
def __init__(self) :
self._theKeys = list()
self._theValues = list()
The __len__ method need only check the size of one of the two lists since they are suppose to always be the same length:
def __len__(self) :
return len(self._theKeys)
The __contains__ method searches the list of keys to determine if the given key is contained in the map. This can be done by applying the in operator the keys list:
def __contains__(self, key) :
return key in self._theKeys
When adding an entry to a map, we must first determine if the key is already in the map. If it is, then the current value mapped to that key is replaced with the new value passed as an argument. To replace the value, the index of the key is located within the keys list and then used to replace the corresponding data value within the values list. If there is no entry with the given key, a new entry consisting of the corresponding key and value components must be added. This is done by appending the key to the end of the keys list and appending the value to the end of the values list. Both lists must always contain the same number of items since corresponding elements between the two lists represent key/value pairs. The implementation of the add method follows:
def add(self, key, value) :
if key in self :
ndx = self._theKeys.index(key)
self._theValues[ndx] = value
return False
else :
self._theKeys.append(key)
self._theValues.append(value)
return True
The implementation of the Map class using parallel lists is provided in the listing below. The implementation of the remaining methods are left as an exercise.
Program Listing
# Implementation of the Map ADT using parallel lists. class Map : # Creates an empty map instance. def __init__(self) : # One list is for the keys, the other for the values. self._theKeys = list() self._theValues = list() # Returns the number of entries in the map. def __len__(self) : return len(self._theKeys) # Determines if the map contains the given key. def __contains__(self, key) : return key in self._theKeys # Adds a new entry to the map if the key does exist. Otherwise, the # new value replaces the current value associated with the key. def add(self, key, value) : # Is the key in the map? if key in self : # if so, overwrite the its value. ndx = self._theKeys.index(key) self._theValues[ndx] = value return False else : # if not, add a new entry by appending the components. self._theKeys.append(key) self._theValues.append(value) return True # --- The remaining methods go here. --- # Returns an iterator for traversing the keys in the map. def __iter__(self) : return iter(self._theKeys)
|