Sometimes it may be necessary to take two sorted lists and merge them to create a new sorted list. Consider the following code segment:
listA = [ 2, 8, 15, 23, 37 ]
listB = [ 4, 6, 15, 20 ]
newList = mergeSortedLists(listA, listB)
print(newList)
which creates two lists with the items ordered in ascending order and then calls a user-defined function to create and return a new list created by merging the other two. Printing the new merged list produces
[2, 4, 6, 8, 15, 15, 20, 23, 37]
Problem Solution
This problem can be solved by simulating the action a person might take to merge two stacks of exam papers, each of which are in alphabetical order. Start by choosing the exam from the two stacks with the name that comes first in alphabetical order. Flip it over on the table to start a new stack. Again, choose the exam from the top of the two stacks that comes next in alphabetical order and flip it over and place it on top of first one. Repeat this process until one of the two original stacks is exhausted. The exams in the remaining stack can be flipped over on top of the new stack as they are already in alphabetical order and alphabetically follow the last exam flipped onto the new stack. You now have a single stack of exams in alphabetical order.
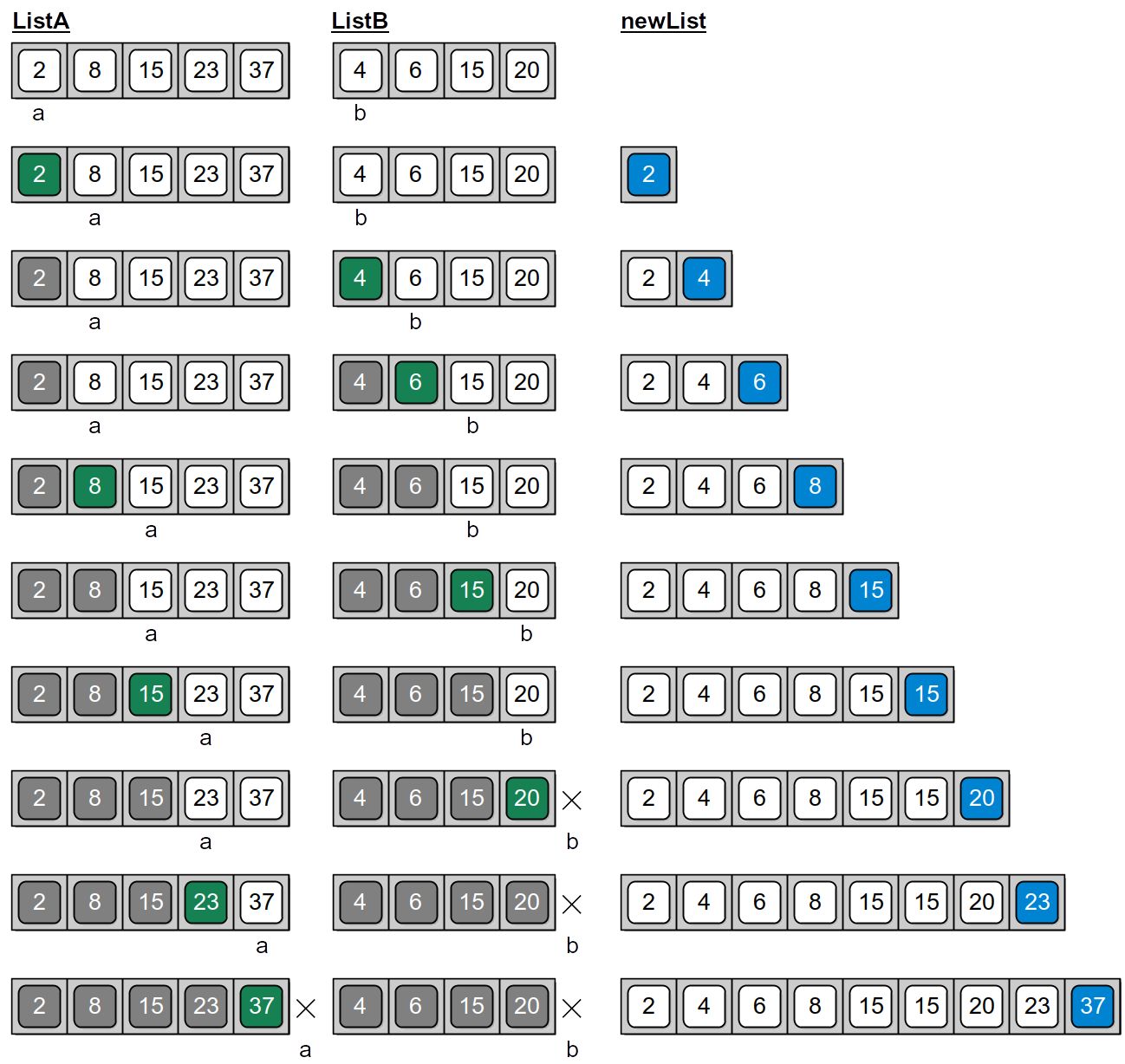
A similar approach can be used to merge two sorted lists. Consider the illustration in Figure 6.9.1, which demonstrates this process on the sample lists created in the example code segment above.
Figure 6.9.1: 'The steps for merging two sorted lists into a new sorted list.
a and b are index variables indicating the next value to be merged from the respective list.'
The items in the original list are not removed, but instead copied to the new list. Thus, there is no "top" item from which to select the smallest value as was the case in the example of merging two stacks of exams. Instead, index variables are used to indicate the "top" or next value within each list. The implementation of the mergeSortedLists function is provided below.
Program Listing
# Merges two sorted lists to create and return a new sorted list. def mergeSortedLists( listA, listB ) : # Create the new list and initialize the list markers. newList = list() a = 0 b = 0 # Merge the two lists together until one is empty. while a < len( listA ) and b < len( listB ) : if listA[a] < listB[b] : newList.append( listA[a] ) a += 1 else : newList.append( listB[b] ) b += 1 # If listA contains more items, append them to newList. while a < len( listA ) : newList.append( listA[a] ) a += 1 # Or if listB contains more items, append them to newList. while b < len( listB ) : newList.append( listB[b] ) b += 1 return newList
|
The process of merging the two lists begins by creating a new empty list and initializing the two index variables to zero. A loop is used to repeat the process of selecting the next largest value to be added to the new merged list. During the iteration of the loop, the value at listA[a] is compared to the value listB[b]. The largest of these two values is added or appended to the new list. If the two values are equal, the value from listB is chosen. As values are copied from the two original lists to the new merged list, one of the two index variables a or b is incremented to indicate the next largest value in the corresponding list.
This process is repeated until all of the values have been copied from one of the two lists, which occurs when a equals the length of listA or b equals the length of listB. Note that we could have created and initialized the new list with a sufficient number of elements to store all of the items from both listA and listB. While that works for this specific problem, we want to create a more general solution that we can easily modify for similar problems where the new list may not contain all of the items from the other two lists.
After the first loop terminates, one of the two lists will be empty and one will contain at least one additional value. All of the values remaining in that list must be copied to the new merged list. This is done by the next two while loops, but only one will be executed depending on which list contains additional values. The position containing the next value to be copied is denoted by the respective index variable a or b.
Run Time Analysis

merging sorted lists
To evaluate the solution for merging two sorted list, assume listA and
listB each contain items. The analysis depends on the number of
iterations performed by each of the three loops, all of which perform the
same action of copying a value from one of the two original lists to the new
merged list. The first loop iterates until all of the values in one of the
two original lists have been copied to the third. After the first loop
terminates, only one of the next two loops will be executed, depending on
which list still contains values.
- The first loop performs the maximum number of iterations when the selection of the next value to be copied alternates between the two lists. This results in all values from either
listA or listB being copied to the newList and all but one value from the other for a total of iterations. Then, one of the next two loops will execute a single iteration in order to copy the last value to the newList.
- The minimum number of iterations performed by the first loop occurs when all values from one list are copied to the
newList and none from the other. If the first loop copies the entire contents of listA to the newList, it will require iterations followed by iterations of the third loop to copy the values from listB. If the first loop copies the entire contents of listB to the newList, it will require iterations followed by iterations of the second loop to copy the values from listA.
In both cases, the three loops are executed for a combined total of iterations. Since the statements performed by each of the three loops all require constant time, merging two lists can be done in time.